Java Delta Photo Compression
Find the difference of two pics.
eg.
from:
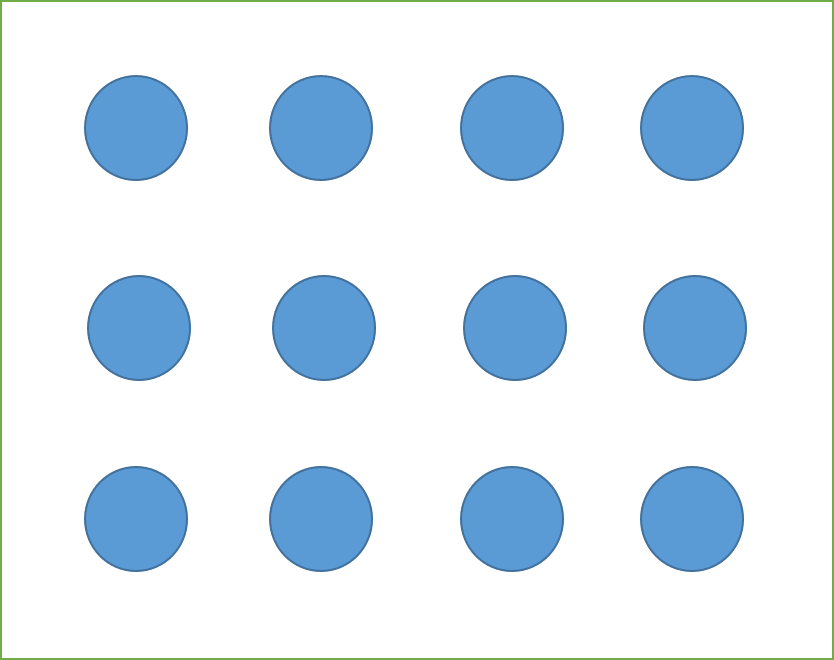
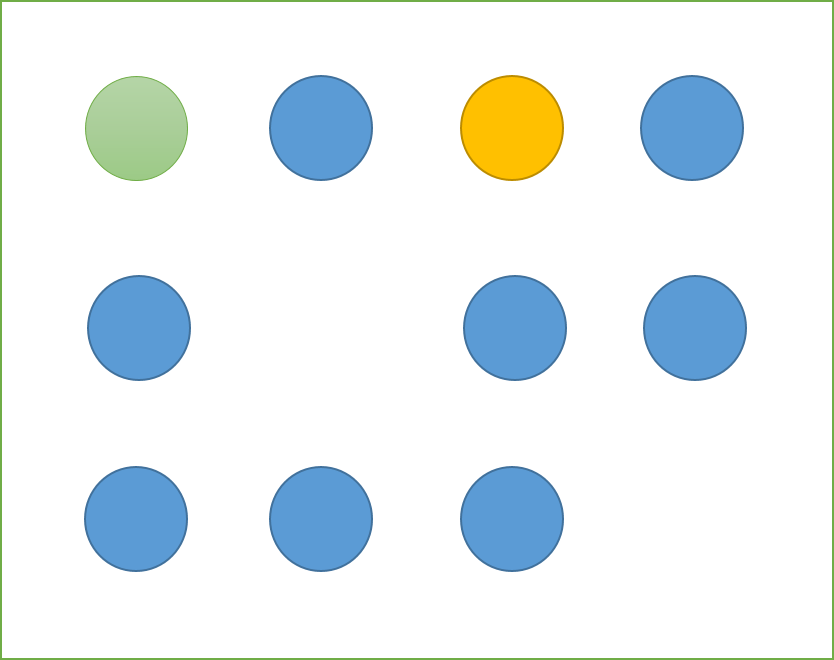
to:
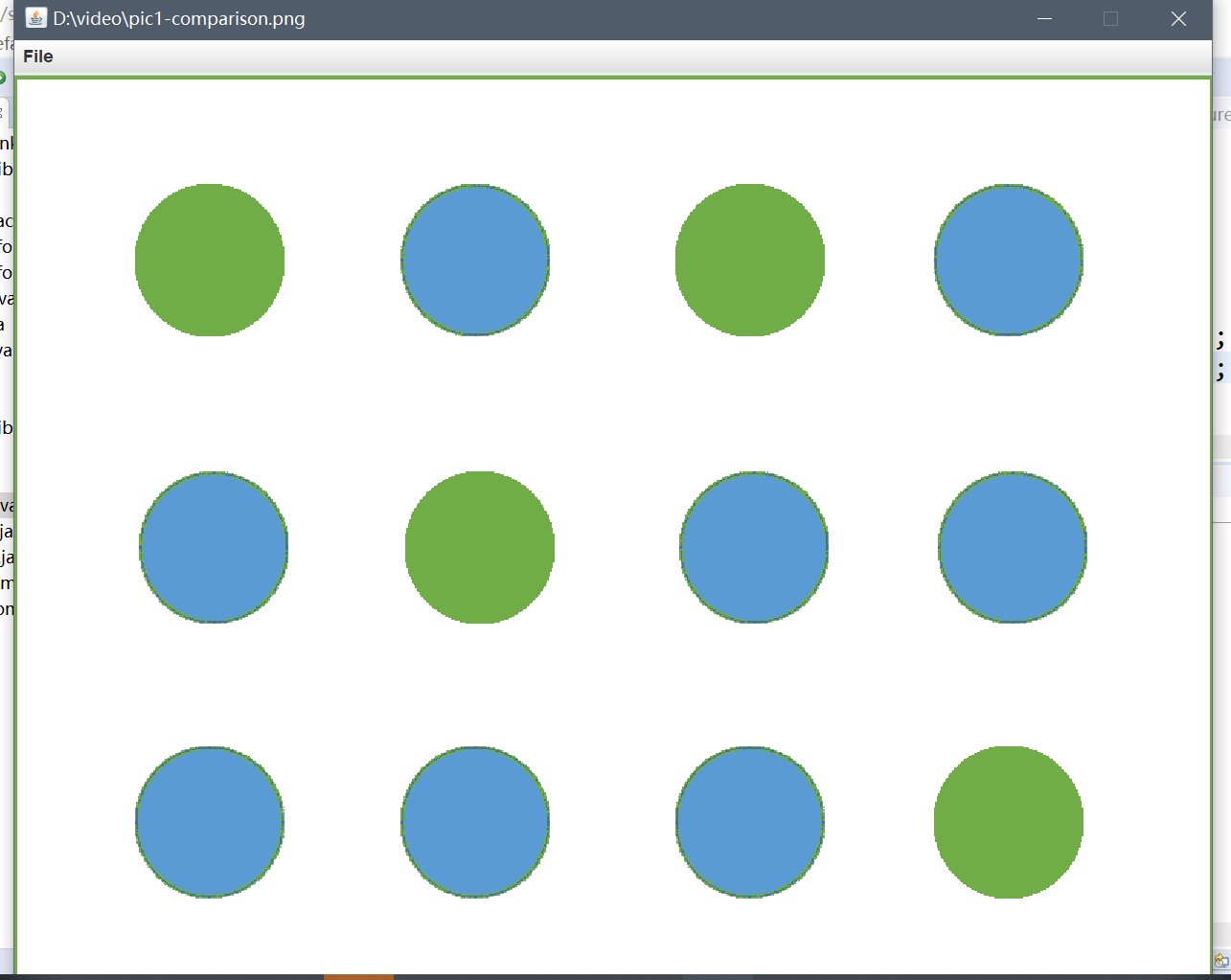
Delta.java
package compression;
import java.awt.*;
public class Delta {
public static void main(String[] args){
Picture pic1 = new Picture("D:\\video\\pic1-comparison.png");
Picture pic2 = new Picture("D:\\video\\pic2-comparison.png");
for(int i = 0; i < pic1.width(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < pic1.height(); j++){
Color color1 = pic1.get(i,j);
Color color2 = pic2.get(i,j);
if(!(color1.equals(color2))){
StdOut.println("( "+i +" "+ j + "(" + color1.getRed() +" ,"+ color1.getGreen() + "," + color1.getBlue() +")"
+ "(" + color2.getRed() +" ,"+ color2.getGreen() + "," + color2.getBlue() +")" );
pic1.set(i,j, Color.red);
}
}
}
pic1.show();
}
}
Picture.java
package compression;
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Picture.java
* Execution: java Picture imagename
* Dependencies: none
*
* Data type for manipulating individual pixels of an image. The original
* image can be read from a file in JPG, GIF, or PNG format, or the
* user can create a blank image of a given dimension. Includes methods for
* displaying the image in a window on the screen or saving to a file.
*
* % java Picture mandrill.jpg
*
* Remarks
* -------
* - pixel (x, y) is column x and row y, where (0, 0) is upper left
*
******************************************************************************/
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.FileDialog;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JMenuItem;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.KeyStroke;
/**
* This class provides methods for manipulating individual pixels of
* an image using the RGB color format. The alpha component (for transparency)
* is not currently supported.
* The original image can be read from a {@code PNG}, {@code GIF},
* or {@code JPEG} file or the user can create a blank image of a given dimension.
* This class includes methods for displaying the image in a window on
* the screen or saving it to a file.
* <p>
* Pixel (<em>col</em>, <em>row</em>) is column <em>col</em> and row <em>row</em>.
* By default, the origin (0, 0) is the pixel in the top-left corner,
* which is a common convention in image processing.
* The method {@link #setOriginLowerLeft()} change the origin to the lower left.
* <p>
* The {@code get()} and {@code set()} methods use {@link Color} objects to get
* or set the color of the specified pixel.
* The {@code getRGB()} and {@code setRGB()} methods use a 32-bit {@code int}
* to encode the color, thereby avoiding the need to create temporary
* {@code Color} objects. The red (R), green (G), and blue (B) components
* are encoded using the least significant 24 bits.
* Given a 32-bit {@code int} encoding the color, the following code extracts
* the RGB components:
* <blockquote><pre>
* int r = (rgb >> 16) & 0xFF;
* int g = (rgb >> 8) & 0xFF;
* int b = (rgb >> 0) & 0xFF;
* </pre></blockquote>
* Given the RGB components (8-bits each) of a color,
* the following statement packs it into a 32-bit {@code int}:
* <blockquote><pre>
* int rgb = (r << 16) + (g << 8) + (b << 0);
* </pre></blockquote>
* <p>
* A <em>W</em>-by-<em>H</em> picture uses ~ 4 <em>W H</em> bytes of memory,
* since the color of each pixel is encoded as a 32-bit <code>int</code>.
* <p>
* For additional documentation, see
* <a href="https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/31datatype">Section 3.1</a> of
* <i>Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach</i>
* by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
* See {@link GrayscalePicture} for a version that supports grayscale images.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public final class Picture implements ActionListener {
private BufferedImage image; // the rasterized image
private JFrame frame; // on-screen view
private String filename; // name of file
private boolean isOriginUpperLeft = true; // location of origin
private final int width, height; // width and height
/**
* Creates a {@code width}-by-{@code height} picture, with {@code width} columns
* and {@code height} rows, where each pixel is black.
*
* @param width the width of the picture
* @param height the height of the picture
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code width} is negative or zero
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code height} is negative or zero
*/
public Picture(int width, int height) {
if (width <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("width must be positive");
if (height <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("height must be positive");
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
image = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// set to TYPE_INT_ARGB here and in next constructor to support transparency
}
/**
* Creates a new picture that is a deep copy of the argument picture.
*
* @param picture the picture to copy
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code picture} is {@code null}
*/
public Picture(Picture picture) {
if (picture == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("constructor argument is null");
width = picture.width();
height = picture.height();
image = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
filename = picture.filename;
isOriginUpperLeft = picture.isOriginUpperLeft;
for (int col = 0; col < width(); col++)
for (int row = 0; row < height(); row++)
image.setRGB(col, row, picture.image.getRGB(col, row));
}
/**
* Creates a picture by reading an image from a file or URL.
*
* @param name the name of the file (.png, .gif, or .jpg) or URL.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if cannot read image
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code name} is {@code null}
*/
public Picture(String name) {
if (name == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("constructor argument is null");
this.filename = name;
try {
// try to read from file in working directory
File file = new File(name);
if (file.isFile()) {
image = ImageIO.read(file);
}
else {
// resource relative to .class file
URL url = getClass().getResource(filename);
// resource relative to classloader root
if (url == null) {
url = getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(name);
}
// or URL from web
if (url == null) {
url = new URL(name);
}
image = ImageIO.read(url);
}
if (image == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("could not read image: " + name);
}
width = image.getWidth(null);
height = image.getHeight(null);
}
catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("could not open image: " + name, ioe);
}
}
/**
* Creates a picture by reading the image from a PNG, GIF, or JPEG file.
*
* @param file the file
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if cannot read image
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code file} is {@code null}
*/
public Picture(File file) {
if (file == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("constructor argument is null");
try {
image = ImageIO.read(file);
}
catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("could not open file: " + file, ioe);
}
if (image == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("could not read file: " + file);
}
width = image.getWidth(null);
height = image.getHeight(null);
filename = file.getName();
}
/**
* Returns a {@link JLabel} containing this picture, for embedding in a {@link JPanel},
* {@link JFrame} or other GUI widget.
*
* @return the {@code JLabel}
*/
public JLabel getJLabel() {
if (image == null) return null; // no image available
ImageIcon icon = new ImageIcon(image);
return new JLabel(icon);
}
/**
* Sets the origin to be the upper left pixel. This is the default.
*/
public void setOriginUpperLeft() {
isOriginUpperLeft = true;
}
/**
* Sets the origin to be the lower left pixel.
*/
public void setOriginLowerLeft() {
isOriginUpperLeft = false;
}
/**
* Displays the picture in a window on the screen.
*/
public void show() {
// create the GUI for viewing the image if needed
if (frame == null) {
frame = new JFrame();
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
JMenu menu = new JMenu("File");
menuBar.add(menu);
JMenuItem menuItem1 = new JMenuItem(" Save... ");
menuItem1.addActionListener(this);
// use getMenuShortcutKeyMaskEx() in Java 10 (getMenuShortcutKeyMask() deprecated)
menuItem1.setAccelerator(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke(KeyEvent.VK_S,
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getMenuShortcutKeyMask()));
menu.add(menuItem1);
frame.setJMenuBar(menuBar);
frame.setContentPane(getJLabel());
// f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
if (filename == null) frame.setTitle(width + "-by-" + height);
else frame.setTitle(filename);
frame.setResizable(false);
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
// draw
frame.repaint();
}
/**
* Returns the height of the picture.
*
* @return the height of the picture (in pixels)
*/
public int height() {
return height;
}
/**
* Returns the width of the picture.
*
* @return the width of the picture (in pixels)
*/
public int width() {
return width;
}
private void validateRowIndex(int row) {
if (row < 0 || row >= height())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("row index must be between 0 and " + (height() - 1) + ": " + row);
}
private void validateColumnIndex(int col) {
if (col < 0 || col >= width())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("column index must be between 0 and " + (width() - 1) + ": " + col);
}
/**
* Returns the color of pixel ({@code col}, {@code row}) as a {@link java.awt.Color}.
*
* @param col the column index
* @param row the row index
* @return the color of pixel ({@code col}, {@code row})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless both {@code 0 <= col < width} and {@code 0 <= row < height}
*/
public Color get(int col, int row) {
validateColumnIndex(col);
validateRowIndex(row);
int rgb = getRGB(col, row);
return new Color(rgb);
}
/**
* Returns the color of pixel ({@code col}, {@code row}) as an {@code int}.
* Using this method can be more efficient than {@link #get(int, int)} because
* it does not create a {@code Color} object.
*
* @param col the column index
* @param row the row index
* @return the integer representation of the color of pixel ({@code col}, {@code row})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless both {@code 0 <= col < width} and {@code 0 <= row < height}
*/
public int getRGB(int col, int row) {
validateColumnIndex(col);
validateRowIndex(row);
if (isOriginUpperLeft) return image.getRGB(col, row);
else return image.getRGB(col, height - row - 1);
}
/**
* Sets the color of pixel ({@code col}, {@code row}) to given color.
*
* @param col the column index
* @param row the row index
* @param color the color
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless both {@code 0 <= col < width} and {@code 0 <= row < height}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code color} is {@code null}
*/
public void set(int col, int row, Color color) {
validateColumnIndex(col);
validateRowIndex(row);
if (color == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("color argument is null");
int rgb = color.getRGB();
setRGB(col, row, rgb);
}
/**
* Sets the color of pixel ({@code col}, {@code row}) to given color.
*
* @param col the column index
* @param row the row index
* @param rgb the integer representation of the color
* @throws IllegalArgumentException unless both {@code 0 <= col < width} and {@code 0 <= row < height}
*/
public void setRGB(int col, int row, int rgb) {
validateColumnIndex(col);
validateRowIndex(row);
if (isOriginUpperLeft) image.setRGB(col, row, rgb);
else image.setRGB(col, height - row - 1, rgb);
}
/**
* Returns true if this picture is equal to the argument picture.
*
* @param other the other picture
* @return {@code true} if this picture is the same dimension as {@code other}
* and if all pixels have the same color; {@code false} otherwise
*/
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (other == this) return true;
if (other == null) return false;
if (other.getClass() != this.getClass()) return false;
Picture that = (Picture) other;
if (this.width() != that.width()) return false;
if (this.height() != that.height()) return false;
for (int col = 0; col < width(); col++)
for (int row = 0; row < height(); row++)
if (this.getRGB(col, row) != that.getRGB(col, row)) return false;
return true;
}
/**
* Returns a string representation of this picture.
* The result is a <code>width</code>-by-<code>height</code> matrix of pixels,
* where the color of a pixel is represented using 6 hex digits to encode
* the red, green, and blue components.
*
* @return a string representation of this picture
*/
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(width +"-by-" + height + " picture (RGB values given in hex)\n");
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
int rgb = 0;
if (isOriginUpperLeft) rgb = image.getRGB(col, row);
else rgb = image.getRGB(col, height - row - 1);
sb.append(String.format("#%06X ", rgb & 0xFFFFFF));
}
sb.append("\n");
}
return sb.toString().trim();
}
/**
* This operation is not supported because pictures are mutable.
*
* @return does not return a value
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if called
*/
public int hashCode() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("hashCode() is not supported because pictures are mutable");
}
/**
* Saves the picture to a file in either PNG or JPEG format.
* The filetype extension must be either .png or .jpg.
*
* @param name the name of the file
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code name} is {@code null}
*/
public void save(String name) {
if (name == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to save() is null");
save(new File(name));
filename = name;
}
/**
* Saves the picture to a file in a PNG or JPEG image format.
*
* @param file the file
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code file} is {@code null}
*/
public void save(File file) {
if (file == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("argument to save() is null");
filename = file.getName();
if (frame != null) frame.setTitle(filename);
String suffix = filename.substring(filename.lastIndexOf('.') + 1);
if ("jpg".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix) || "png".equalsIgnoreCase(suffix)) {
try {
ImageIO.write(image, suffix, file);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Error: filename must end in .jpg or .png");
}
}
/**
* Opens a save dialog box when the user selects "Save As" from the menu.
*/
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
FileDialog chooser = new FileDialog(frame,
"Use a .png or .jpg extension", FileDialog.SAVE);
chooser.setVisible(true);
if (chooser.getFile() != null) {
save(chooser.getDirectory() + File.separator + chooser.getFile());
}
}
/**
* Unit tests this {@code Picture} data type.
* Reads a picture specified by the command-line argument,
* and shows it in a window on the screen.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Picture picture = new Picture(args[0]);
System.out.printf("%d-by-%d\n", picture.width(), picture.height());
picture.show();
}
}
StdOot.java
package compression;
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac StdOut.java
* Execution: java StdOut
* Dependencies: none
*
* Writes data of various types to standard output.
*
******************************************************************************/
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Locale;
/**
* This class provides methods for printing strings and numbers to standard output.
* <p>
* <b>Getting started.</b>
* To use this class, you must have {@code StdOut.class} in your
* Java classpath. If you used our autoinstaller, you should be all set.
* Otherwise, either download
* <a href = "https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/code/stdlib.jar">stdlib.jar</a>
* and add to your Java classpath or download
* <a href = "https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/stdlib/StdOut.java">StdOut.java</a>
* and put a copy in your working directory.
* <p>
* Here is an example program that uses {@code StdOut}:
* <pre>
* public class TestStdOut {
* public static void main(String[] args) {
* int a = 17;
* int b = 23;
* int sum = a + b;
* StdOut.println("Hello, World");
* StdOut.printf("%d + %d = %d\n", a, b, sum);
* }
* }
* </pre>
* <p>
* <b>Differences with System.out.</b>
* The behavior of {@code StdOut} is similar to that of {@link System#out},
* but there are a few technical differences:
* <ul>
* <li> {@code StdOut} coerces the character-set encoding to UTF-8,
* which is a standard character encoding for Unicode.
* <li> {@code StdOut} coerces the locale to {@link Locale#US},
* for consistency with {@link StdIn}, {@link Double#parseDouble(String)},
* and floating-point literals.
* <li> {@code StdOut} <em>flushes</em> standard output after each call to
* {@code print()} so that text will appear immediately in the terminal.
* </ul>
* <p>
* <b>Reference.</b>
* For additional documentation,
* see <a href="https://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/15inout">Section 1.5</a> of
* <em>Computer Science: An Interdisciplinary Approach</em>
* by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public final class StdOut {
// force Unicode UTF-8 encoding; otherwise it's system dependent
private static final String CHARSET_NAME = "UTF-8";
// assume language = English, country = US for consistency with StdIn
private static final Locale LOCALE = Locale.US;
// send output here
private static PrintWriter out;
// this is called before invoking any methods
static {
try {
out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out, CHARSET_NAME), true);
}
catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
// don't instantiate
private StdOut() { }
/**
* Terminates the current line by printing the line-separator string.
*/
public static void println() {
out.println();
}
/**
* Prints an object to this output stream and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the object to print
*/
public static void println(Object x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints a boolean to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the boolean to print
*/
public static void println(boolean x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints a character to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the character to print
*/
public static void println(char x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints a double to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the double to print
*/
public static void println(double x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints an integer to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the integer to print
*/
public static void println(float x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints an integer to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the integer to print
*/
public static void println(int x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints a long to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the long to print
*/
public static void println(long x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints a short integer to standard output and then terminates the line.
*
* @param x the short to print
*/
public static void println(short x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Prints a byte to standard output and then terminates the line.
* <p>
* To write binary data, see {@link BinaryStdOut}.
*
* @param x the byte to print
*/
public static void println(byte x) {
out.println(x);
}
/**
* Flushes standard output.
*/
public static void print() {
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints an object to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the object to print
*/
public static void print(Object x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a boolean to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the boolean to print
*/
public static void print(boolean x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a character to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the character to print
*/
public static void print(char x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a double to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the double to print
*/
public static void print(double x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a float to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the float to print
*/
public static void print(float x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints an integer to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the integer to print
*/
public static void print(int x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a long integer to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the long integer to print
*/
public static void print(long x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a short integer to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the short integer to print
*/
public static void print(short x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a byte to standard output and flushes standard output.
*
* @param x the byte to print
*/
public static void print(byte x) {
out.print(x);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a formatted string to standard output, using the specified format
* string and arguments, and then flushes standard output.
*
*
* @param format the <a href = "http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Formatter.html#syntax">format string</a>
* @param args the arguments accompanying the format string
*/
public static void printf(String format, Object... args) {
out.printf(LOCALE, format, args);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Prints a formatted string to standard output, using the locale and
* the specified format string and arguments; then flushes standard output.
*
* @param locale the locale
* @param format the <a href = "http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/Formatter.html#syntax">format string</a>
* @param args the arguments accompanying the format string
*/
public static void printf(Locale locale, String format, Object... args) {
out.printf(locale, format, args);
out.flush();
}
/**
* Unit tests some of the methods in {@code StdOut}.
*
* @param args the command-line arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// write to stdout
StdOut.println("Test");
StdOut.println(17);
StdOut.println(true);
StdOut.printf("%.6f\n", 1.0/7.0);
}
}
Written on October 16, 2019